The Value of Our Research
A large satellite typically incorporates more than about 100,000-1,000,000 different space-qualified parts. Space-qualified electronics, for example, are assembled using a wide variety of space-qualified parts. A satellite cannot be completed if any part is unavailable.
The functionality of parts substantially limits what satellite systems can accomplish. The improved performance and functionality of the systems hinge on improved space-qualified parts.
To reach the two objectives of maintaining Japan's own space missions and enhancing the competitiveness of Japanese satellites, we will develop parts strategically selected in JAXA's Parts Program.
Research Goals
Some of our R&D activities at JAXA have focused on parts critical to the functionality and performance of a satellite. Specifically, we seek to optimize the following types of strategic, space-qualified parts.
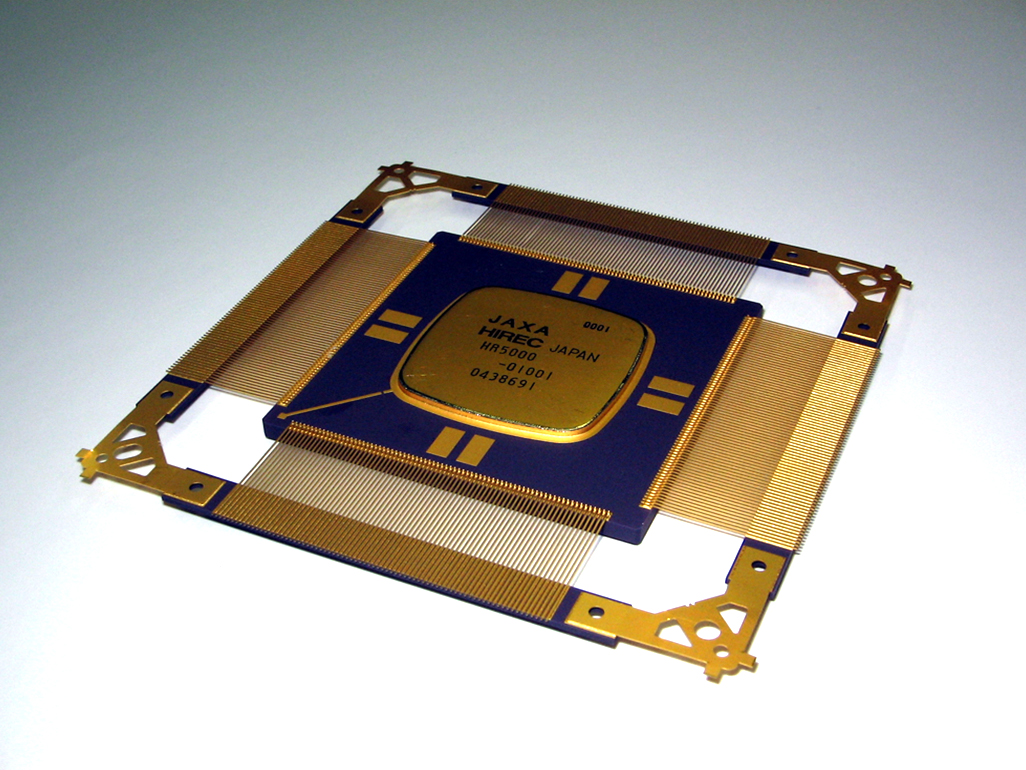
Space-qualified user programming device
To meet diversifying, high-level space mission requirements flexibly, we are leveraging JAXA's expertise in microprocessor circuit design to mature a domestically developed SOI*1- ASIC*2 technology for use in space missions over the next five years.
Now we are promoting research on “Radiation Hardness By Design methodology (RHBD) ” of ultra-miniaturized semiconductor devices for next decade space missions.And also, aiming to realize on-orbit reprogramming technology, we are promoting research on low power non-volatile memory technology (such as nanobridge technology) .
*1 SOI: Semiconductor device in which a silicon semiconductor layer is formed on an insulator layer
*2 ASIC: A kind of integrated circuit that is designed and built for a specific application or purpose
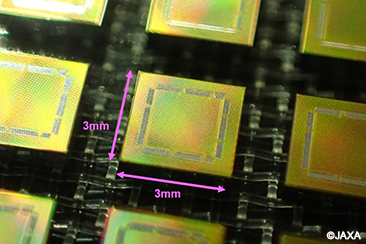
Evaluation of cutting-edge commercial parts technologies for satellite application (Small package, Surface mount technology)
Now we are promoting cutting-edge commercial parts technologies used for mobile equipment to use satellite equipment.
We are focusing on how to apply small packaging technology and 3-dimensional high-density surface mounting technology for future high performance and small satellites.
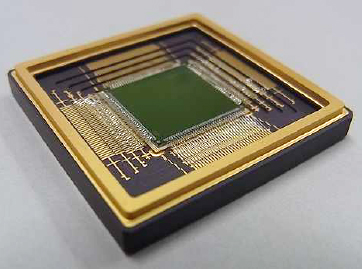
Space-qualified parts with power consumption reduced by more than 80%
We are applying compound semiconductors to develop a higher-efficiency, lower-loss power switching device for a power converter and controller power device over the next few years.
Looking a decade ahead, we are also researching semiconductor technologies to develop normally-off computing that will enable an ultra-low-power space-qualified device.